Post-Failover Options
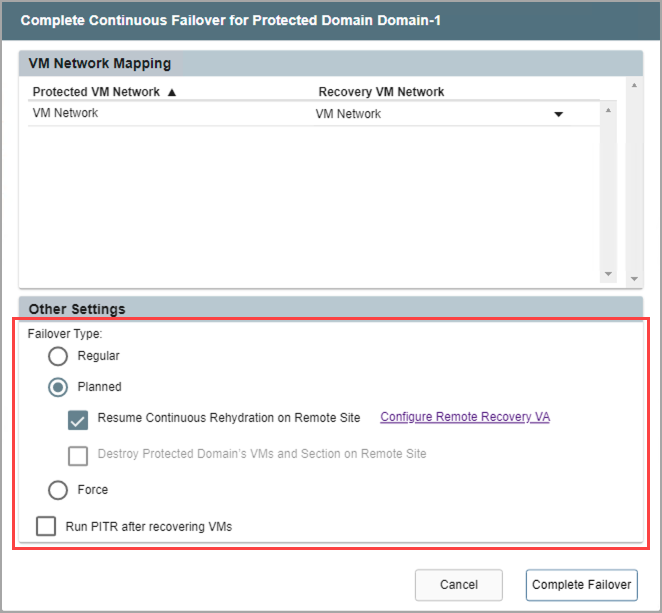
Multiple options are available to control the state of the protected site and ownership of VMs and data after failover has been completed. Failover can be completed in one of three ways: regular, planned, or forced.
Modes to complete failover.
- Regular Failover: Follows the set course of steps for normal failover mode.
- Planned Failover: Shuts down the domain at the protected site (gracefully) before transferring ownership of VMs and data to the recovery site.
- Data at the protected site will not be deleted.
- Planned failover is typically used for non-disaster related events such as seamlessly shifting the location of VMs and their workloads while they continue to operate (i.e., migration).
- For example, if it is known an event will occur that would produce a large workload or data burst that exceeds the resource capacity of the on-premises site, it could be beneficial to shift the VMs and their workloads to a cloud services provider capable of meeting the demand.
- Another common case is moving VMs and workloads away from the on-premises site before performing major site maintenance that could potentially be disruptive or risky. After maintenance is complete, the VMs and workloads can be non-disruptively “failed-back” to the updated on-premises site.
Note: During planned failover, any running VMs will be gracefully shut down by the MSA. VMware tools should be installed on all protected VMs to ensure proper operation of the shutdown process. If any VMs cannot be automatically shut down by the MSA they will need to be manually powered-off and then the task should be re-run. In general, it is recommended to install VMware tools on all VMs that will be protected.
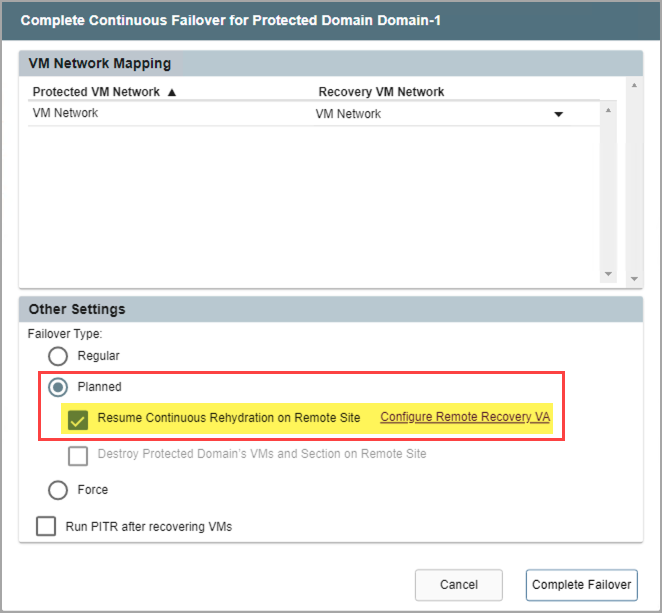
- If planned failover is used, a sub-option is available to Resume Continuous Rehydration on the Remote Site.
- Planned failover using the continuous rehydration option is in essence “continuous failback.” Once VMs and data have been failed over to the recovery site, any new data generated there will automatically be “rehydrated” (synchronized in the background) back to the original protected site allowing for “near-zero RTO” failback.
- Click the Configure Remote Recovery VA link to configure continuous rehydration settings. (It is typically configured to run automatically upon failover.)
Planned failover mode.
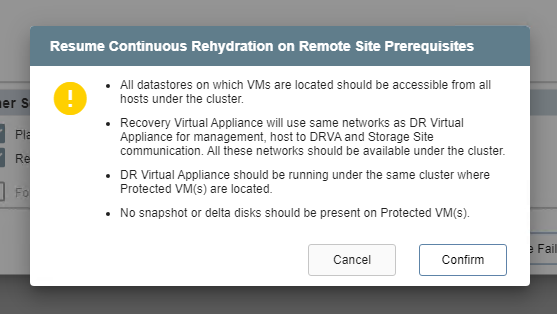
- Certain conditions must be met in order to use the Resume Continuous Rehydration on Remote Site option.
Resume continuous rehydration.
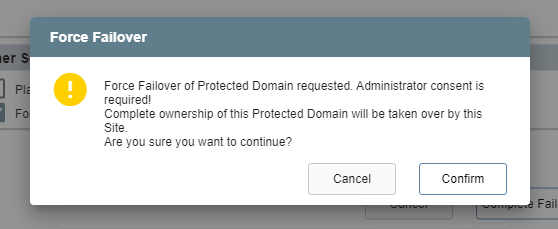
- Forced Failover: Assumes the primary site is no longer accessible.
- Ownership of the protected domain is immediately passed to the recovery site.
- A dialog window will appear asking the user to confirm that complete ownership of the protected domain can be taken over immediately by the recovery site.
Forced failover.