AROVA Configuration Disk (ACD)
When AROVA is deployed, an AROVA Configuration Disk ("ACD") will be created. After the ACD has been replicated to the secondary disk and is active you can begin using the software to protect VMs.
- From the AROVA UI, check ACD replication status and RPO from the Configurations tab.
- When the ACD is created, it is essentially "empty" so there is not much to be replicated to the secondary disk and Initial Sync of the ACD will be very fast.
- Protection can be started immediately after ACD initial synchronization is complete.
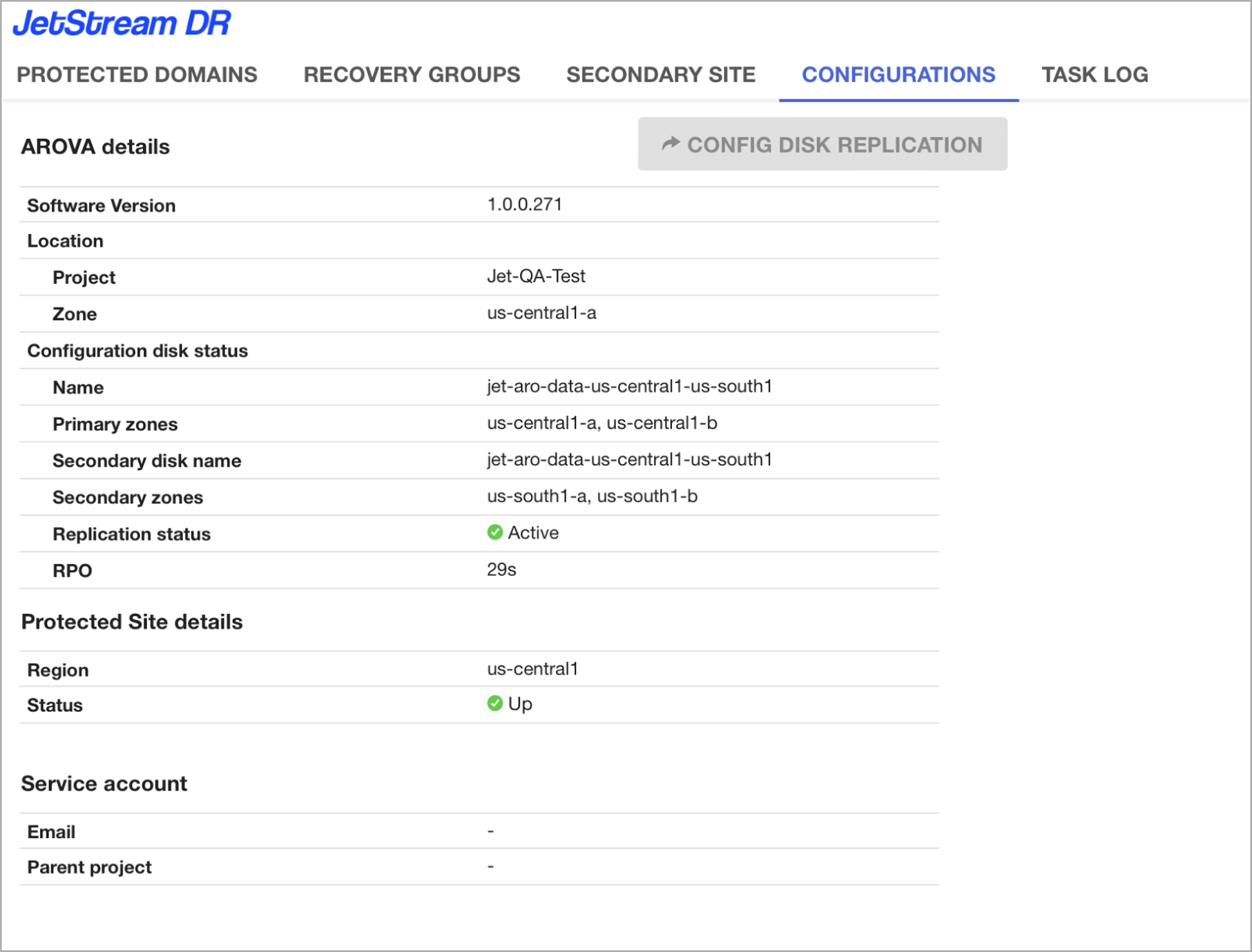
Figure: AROVA Configurations screen.
- It is recommended to frequently monitor AROVA status.
- An AROVA may temporarily become in-operational for various reasons:
- ACD’s R1Z1 disk is down
- Both ACD zones are down
- AROVA process failed (software error) or AROVA was deleted by mistake
- Region failure
- In case of failure, asynchronous data replication for unaffected protected VMs continues but orchestration and VM configuration updates are not functional until AROVA is redeployed.
- If failure occurs while AROVA is not functional and urgent failover is required, recovered VM properties may be stale. (However, this is a low probability double-failure event that is unlikely to be encountered.)
- Handling of these use cases is described in more detail in a later section of this guide.
- In case of AROVA internal events (like ACD replication failure), AROVA delivers errors, warnings, and information messages through the Google Cloud logging infrastructure.
- It is strongly recommended to create native Google Cloud alerts for log messages with logName containing the string “arova-global”.
Also see: